
MozCon 2018: You Don’t Know SEO
The following post is part of WTWH Media Marketing Lab’s ongoing blog series from MozCon 2018. View the full presentation here.
On the last day of MozCon, Michael King, Founder/Managing Director of iPullRank, took the stage to present his talk inspired by a series of books called, “You Don’t Know JavaScript,” written by Kyle Simpson.
King’s presentation goal was to add more color to what’s going on in the background of SEO so marketers could better understand what we’re doing.
Being Effective At Modern SEO Is About Six Things:
- Mobile-first
- Structured Data
- Speed
- Content
- Authority
- Integrated Search
Crawling & Indexing
King began by explaining that Google adheres closely to HTTP response codes and went into further discussion about the 304-response code. The 304 response code is “not modified and when your browser goes to a page that it’s seen before that hasn’t changed since the last time you were on that page, it won’t re-download it,” King explained, “If you use it (304), what you can do is make more out of your crawl allocation. That means they (Google) won’t spend time crawling pages they’ve already seen and crawl more pages on your site that are valuable.” According to a botify study, no one is using 304s. So, King ended indexing and crawling by giving us a little know fact: If you need to increase your crawl rate, there is a section on Google Search Console where you can reach out to the crawl team and ask them to increase crawl rate because of a migration and the team will get it done in the next few days.
JavaScript and SEO
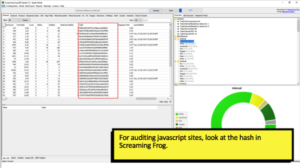
The web rendering service of Google is based on Chrome 41, which doesn’t support everything the latest version of Chrome does. King recommended when auditing JavaScript sites to run some crawls using Screaming Frog. He said to run a text-based crawl and a JavaScript rendering crawl. Then, compare the hash column. The hash column is a representation of all the content on a page. If there are any differences between the columns, you have a problem that you want to look into.
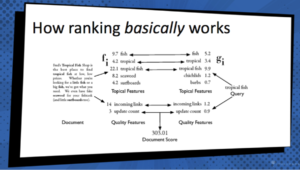
“How Ranking Basically Works”
- Content is broken down into a series of features
- Those features are scored into mathematical models
- Other features are looked at: topical, links, anchor texts
- All of this comprises a score
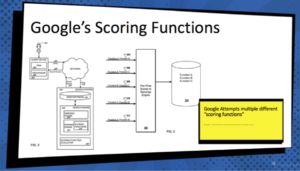
King followed his description of how ranking work with talking about Google’s scoring functions. Google has a series of scoring functions, but King explained, “Even if we knew all of the different equations that they’re using, it looks like they may try different ones for different queries,” Said King.
Hyper-targeted and optimized content
King asked, “So with all this complexity, how can we beat the bots?” His response was hyper-targeted and optimized content. He went on to break down how search engines look at a page:
Tokenization
The search engine will break down the page into sentences and sentences into tokens or individual words. They will then use this in the statistical model for scoring.
Synonyms & Close Variants
Search engines look to see if words that are closely related are used together on the same page. This helps the info retrieval system understand what the page is about. King used the example of stemming. If love, loving, lovingly, loved, lover, and lovely were on the same page; the search engine would break this down into the root of love to better determine relationships and relevance.
Semantic Distance & Term Relationships
The search engine is looking at how physically close the words are together to determine their relationship in statistical models.
King’s informational presentation proved that we can’t know it all but he did improve our understanding of Google. If you’re wondering what other topics King spoke about, I attached a link at the top of the page that will take you to his full presentation.
 Michael King founded boutique digital marketing agency, iPullRank focused on Content Strategy, Machine Learning, SEO, Paid Media, Measurement and Conversion Rate Optimization
Michael King founded boutique digital marketing agency, iPullRank focused on Content Strategy, Machine Learning, SEO, Paid Media, Measurement and Conversion Rate Optimization



Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.